Guide to Accounting for Law: Essential Insights for 2025
Managing finances is one of the most critical and daunting aspects of running a law firm in 2025. Legal professionals face rising complexity in compliance, trust accounting, and the constant risk of costly errors or penalties.
Mastering accounting for law is essential. It empowers firms to increase profitability, maintain compliance, and build client trust. This guide is your essential roadmap to stay ahead in the evolving legal landscape.
You will discover:
Core accounting principles for law firms
Compliance rules and ethical standards
Common mistakes and how to prevent them
Technology solutions for efficiency
Future trends shaping legal accounting
Gain practical steps and updated best practices to make 2025 your most successful year yet.
The Fundamentals of Law Firm Accounting
Understanding the fundamentals of accounting for law is the cornerstone of running a successful legal practice. With growing regulatory demands in 2025, law firms must distinguish between bookkeeping and accounting, comply with evolving standards, and master essential terminology to protect their business and clients.
Key Differences: Legal Bookkeeping vs. Legal Accounting
The foundation of accounting for law begins with understanding the distinct roles of bookkeeping and accounting. Bookkeeping focuses on recording daily transactions, managing ledgers, and reconciling accounts. Accounting, on the other hand, analyzes and interprets financial data, supporting strategic decisions and compliance.
Bookkeeping tasks include:
Recording billable hours and expenses
Managing client payments and disbursements
Reconciling bank accounts and ledgers
Accounting responsibilities involve:
Preparing financial statements and tax forecasts
Interpreting data for business growth
Ensuring compliance with tax and bar regulations
Accurate recordkeeping is vital for compliance and growth. According to the Clio Legal Trends Report, over 60% of small law firms see financial management as their top operational challenge. Both bookkeeping and accounting for law are essential—one maintains data integrity, the other enables informed decision-making. For a deeper dive, explore Bookkeeping for Law Firms.
Why Accounting Matters for Law Firms in 2025
In 2025, the landscape of accounting for law has grown more complex. Regulatory bodies like state bars and the IRS demand strict adherence to evolving rules. Law firms must safeguard client trust by handling funds appropriately and maintaining robust compliance.
Proper accounting for law enables firms to:
Stay ahead of state bar and IRS regulations
Protect client funds through accurate trust accounting
Develop data-driven strategies for resource allocation
Avoid penalties, audits, and reputational harm
Consider the consequences of mishandling IOLTA accounts - such errors can result in severe fines or even disbarment. Beyond compliance, strategic accounting for law is a tool for growth. Firms with strong financial systems can allocate resources more effectively, plan for the future, and secure long-term client relationships.
Legal accounting is not just about avoiding mistakes. It is about building a sustainable, profitable practice that stands out in a competitive market.
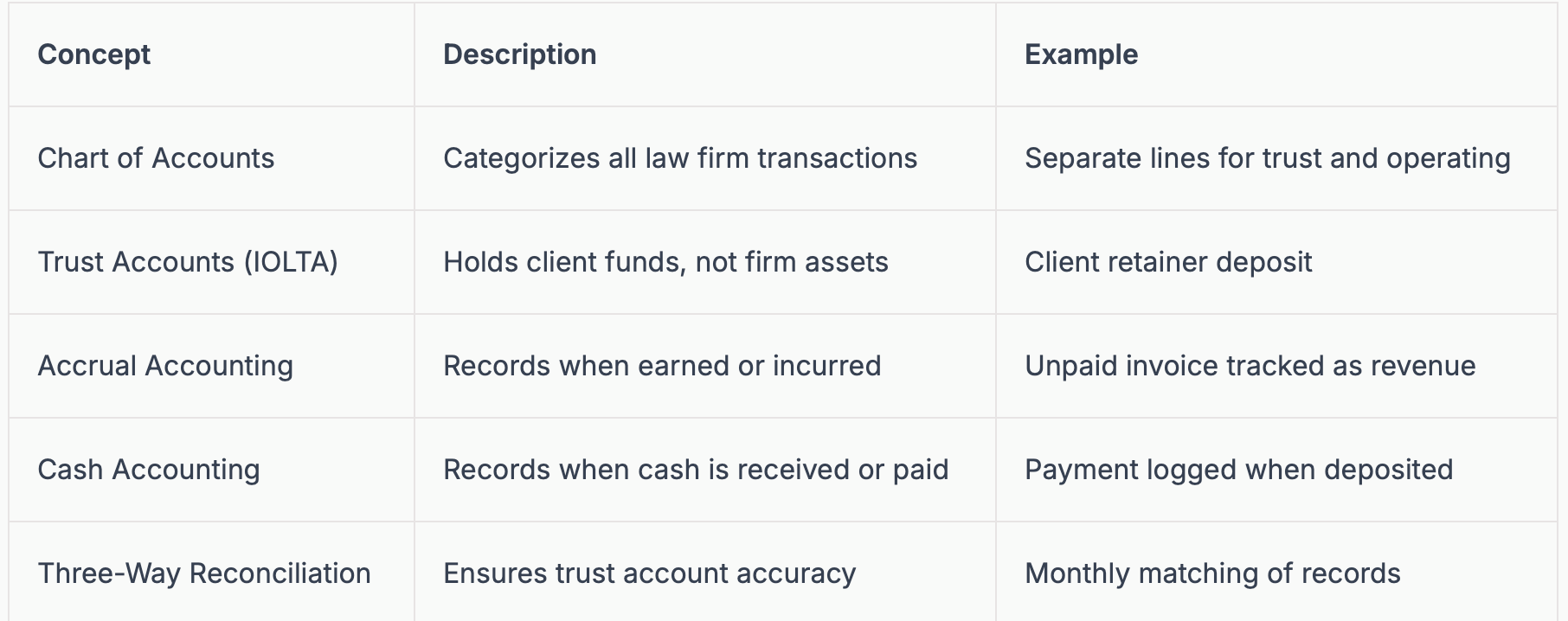
Essential Legal Accounting Terms and Concepts
Mastering accounting for law requires fluency in core terms and processes:
Chart of Accounts: Customizes categories for law firms, such as operating, trust, and client advances.
Trust Accounts (IOLTA): Hold client funds separately, with strict compliance rules to prevent commingling.
Accrual vs. Cash Accounting: Accrual recognizes income and expenses when incurred, cash method when money changes hands. The IRS may require certain methods based on firm size.
Three-Way Reconciliation: Matches bank statements, trust ledgers, and client balances to ensure accuracy.
For instance, a firm may use three-way reconciliation to catch discrepancies before audits. These concepts in accounting for law are the pillars for compliance, risk management, and efficient practice operations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Law Firm Accounting Systems
Setting up a robust accounting system is essential for law firms seeking long-term success. The right approach to accounting for law not only supports compliance but also drives profitability and operational efficiency. Follow these actionable steps to build a solid financial foundation for your legal practice.
1. Establishing the Right Bank Accounts
Every law firm must start by separating business and client finances. Open at least three types of accounts: operating, savings, and trust (IOLTA). This separation is a fundamental principle in accounting for law, protecting both firm assets and client funds from being mixed.
When selecting a bank, ask about fees, security protocols, IOLTA support, and user permission controls. Not all institutions understand the specific needs of legal practices. For example, some banks offer automated alerts if a trust balance falls below a threshold, which can help prevent compliance violations.
A well-structured account system reduces audit flags and streamlines daily operations. According to GrowLaw, firms using separate accounts see a 40% reduction in audit triggers. Regularly review account activity to ensure all deposits and withdrawals are properly allocated.
By making this the first step in your accounting for law systems, you minimize risk and create a strong foundation for compliance and growth.
2. Choosing the Appropriate Accounting Method
Deciding between cash and accrual accounting is a critical early decision. The cash method records transactions when money moves in or out, while the accrual method tracks income and expenses when they are earned or incurred. Each method impacts tax reporting and financial strategy in accounting for law.
IRS and state regulations may dictate which method your firm must use. Many small firms favor the cash method for its simplicity, but as your practice grows, accrual accounting can provide clearer insights into profitability and future cash flow.
For instance, a small firm may use cash accounting for its manageable caseload, but a mid-sized firm might transition to accrual to forecast revenue more accurately. Always consult with a legal accounting professional to ensure your chosen method aligns with jurisdictional rules and supports your business goals.
Choosing the right method for accounting for law ensures accurate reporting and helps avoid compliance pitfalls.
3. Implementing a Robust Bookkeeping System
Bookkeeping is the backbone of accounting for law, capturing every financial transaction accurately. Set up daily processes for tracking billable hours, client payments, expenses, and reimbursements. Use a cloud-based solution to streamline invoice management and minimize manual entry errors.
Monthly bank reconciliations are essential. This step matches your internal records to bank statements, catching discrepancies and potential fraud early. Assign responsibility for reconciliations and ensure they are completed on schedule.
Consider the following best practices:
Categorize all expenses and income by client and matter
Automate recurring transactions where possible
Use secure platforms with audit trails for transparency
A reliable bookkeeping system enables data-driven decisions and keeps your accounting for law organized. Timely, accurate data entry is crucial for both compliance and strategic growth.
4. Trust Accounting Compliance
Handling client funds requires strict adherence to trust accounting rules. Legal professionals must keep client funds in separate IOLTA accounts, never mixing them with firm assets. Promptly transfer earned fees and expenses out of the trust account once billed.
State bar associations require regular reconciliation of trust accounts. The three-way reconciliation process matches bank statements, client ledgers, and the trust ledger to ensure complete accuracy. Document each step and maintain thorough records for audit readiness.
To understand the nuances and avoid common pitfalls, review this Trust Accounting for Law Firms guide. It offers practical advice on staying compliant and highlights the importance of monthly reconciliations.
By prioritizing trust accounting for law, you protect client interests, uphold your reputation, and avoid severe penalties.
5. Record-keeping and Document Management
Effective record-keeping is a non-negotiable part of accounting for law. Maintain clear, organized files for receipts, bank statements, invoices, tax returns, and client ledgers. Decide whether to use digital or paper records, but prioritize security, accessibility, and backup protocols.
Legal document management systems offer encryption, quick search capabilities, and remote access. Digital records cut audit preparation time by 50%, according to Clio, and reduce the risk of lost documents.
Key record-keeping practices include:
Retaining records for the required statutory period
Backing up files regularly, both onsite and in the cloud
Controlling access with user permissions to protect sensitive data
A disciplined approach to document management ensures your accounting for law is audit-ready and efficient, supporting both compliance and client service.
Compliance and Ethics in Law Firm Accounting
Navigating compliance and ethics is at the heart of accounting for law firms. Rigorous attention to evolving rules, ethical obligations, and audit preparedness is essential for every legal practice. In 2025, increased regulatory scrutiny and the complexity of trust accounting make it more critical than ever to maintain robust processes and stay informed.
Understanding State Bar and ABA Regulations
Every law firm must prioritize compliance with both the ABA Model Rule 1.15 and their specific state bar trust accounting rules. These regulations set clear expectations for safeguarding client property, ensuring prompt notification of receipts, and maintaining thorough records. For accounting for law practices, this means a relentless focus on process.
Key compliance obligations include:
Segregating client funds from firm assets at all times
Notifying clients promptly when funds are received
Retaining detailed records for the required retention period
For example, California’s IOLTA rules require monthly reconciliations and strict segregation, while Texas mandates prompt client notification and detailed ledgers. Here is a quick comparison:
Understanding the Three-Way Reconciliation Process is fundamental, as it ensures all trust account records align with bank statements and client ledgers. Regular compliance checks not only prevent disciplinary actions but also build a culture of trust and transparency within the firm.
Common Legal Accounting Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Mistakes in accounting for law practices can lead to severe penalties, loss of licensure, or reputational harm. The most frequent errors include:
Mixing trust and operating funds (commingling)
Failing to reconcile accounts on a regular schedule
Recording client deposits as income before they are earned
Inadequate documentation or lost receipts
Consider a real-world case: a small firm in New York was fined and placed under probation after failing to perform monthly trust account reconciliations, resulting in a shortfall. This highlights the importance of proactive systems.
The best defense is a layered one:
Train all staff on ethical and compliance standards unique to accounting for law
Implement checklists for monthly reconciliations and documentation
Use technology to automate reminders and flag discrepancies
Firms that encourage a culture of compliance and invest in ongoing training significantly reduce their risk profile.
Audit Readiness and Risk Management
Preparing for audits is a non-negotiable part of accounting for law firms. Audits can be random or triggered by client complaints, making it vital to maintain audit trails such as transaction logs, client ledgers, and bank statements.
Internal controls, like having separate approval processes for disbursements and regular peer reviews, help catch errors early. Periodic self-audits reinforce compliance and keep the firm ready for external review.
Firms that prioritize audit readiness experience less disruption and greater confidence in their financial integrity. A diligent approach to risk management not only protects against penalties but also strengthens the foundation of trust that is vital in accounting for law.
Leveraging Technology for Legal Accounting Efficiency
Technology is rapidly transforming accounting for law, providing law firms with tools to simplify compliance, boost accuracy, and streamline workflows. In 2025, embracing the right digital solutions is not just a convenience but a necessity for staying competitive and meeting regulatory demands.
Legal Accounting Software: Features and Benefits
Specialized software is at the heart of effective accounting for law. These platforms are designed to handle unique legal requirements like trust accounting, three-way reconciliation, and client fund management. Key features include automated trust account tracking, seamless billing, customizable reporting, and compliance checks tailored to state bar regulations.
Benefits extend far beyond convenience. Legal accounting software reduces manual errors, shortens reconciliation cycles, and provides real-time financial snapshots. Many platforms now offer cloud access, enabling secure, remote work environments. Choosing the right software can be challenging, given the variety of options available. For an in-depth comparison of leading solutions and insight into whether software or a bookkeeper is best for your practice, refer to this Legal Accounting Software Comparison.
Selecting robust software ensures your accounting for law is efficient, accurate, and audit-ready.
Integration with Practice Management Tools
Integration is essential for maximizing the value of accounting for law. Modern law firms benefit from syncing their accounting systems with practice management tools that handle time tracking, billing, and client communications. This unified approach eliminates redundant data entry and reduces the risk of inconsistencies between systems.
By integrating accounting for law with case management platforms, firms gain real-time visibility into billable hours, expenses, and trust balances. Automated workflows trigger invoices when milestones are reached or alert staff to unpaid balances. This seamless connection empowers firms to make informed decisions and respond quickly to client needs.
The result is a more cohesive, efficient operation that supports compliance and enhances client satisfaction.
Automation and AI in Law Firm Financial Management
Automation and artificial intelligence are reshaping accounting for law, allowing firms to streamline repetitive tasks and gain actionable insights. Automated invoicing, payment reminders, and expense categorization reduce staff workload and help ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
AI-driven tools now provide predictive analytics for cash flow forecasting and risk assessment. These capabilities enable law firms to anticipate financial challenges and adjust strategies proactively. Automated reconciliation, for example, matches transactions across accounts in moments, flagging discrepancies that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Embracing automation and AI in accounting for law positions firms ahead of the curve, delivering efficiency and accuracy that manual processes cannot match.
Data Security and Confidentiality
Protecting sensitive financial and client information is a cornerstone of accounting for law. Legal practices must comply with strict data privacy standards, including GDPR and HIPAA, to maintain client trust and regulatory compliance.
Modern accounting for law platforms employ encryption, role-based access controls, and secure cloud storage to safeguard data. Implementing two-factor authentication adds another layer of protection, ensuring only authorized users access critical financial systems. Regular backups and audit logs further enhance security by preserving records and supporting transparency.
Staying vigilant about data security in accounting for law not only protects your firm but also demonstrates a commitment to ethical and professional standards.
Best Practices and Strategic Insights for 2025
Mastering accounting for law is a cornerstone of running a successful and compliant legal practice in 2025. The landscape is evolving quickly, and law firms must adapt their financial strategies to remain competitive, resilient, and client-focused.
Building a Financially Resilient Law Firm
Financial resilience starts with setting clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) tailored to your practice areas. Law firm leaders should use accounting for law to drive budgeting, forecasting, and cash flow management. Tracking these metrics helps firms anticipate challenges and allocate resources efficiently.
A practical approach is to use digital dashboards to monitor profitability by case type or attorney. This enables quick adjustments when market conditions shift. According to Law Firm Finance Trends and Predictions for 2025, proactive financial management is increasingly vital as regulatory demands and client expectations rise.
Firms that prioritize accounting for law position themselves for long-term sustainability. Regular financial reviews, scenario planning, and technology adoption are all essential steps. By embedding these best practices, firms can weather uncertainty and seize new opportunities.
Training and Delegation: Roles in Law Firm Finance
Effective accounting for law hinges on the expertise of your financial team. Hiring qualified bookkeepers and accountants with experience in legal compliance ensures accuracy and reduces risk. Consider providing ongoing training in compliance, ethical recordkeeping, and technology tools.
Outsourcing certain tasks, such as monthly reconciliations or payroll, can be cost-effective for smaller practices. However, maintaining some in-house oversight is critical for quality control. Firms that invest in dedicated financial staff see a 35% reduction in errors, highlighting the value of specialization.
When delegating accounting for law responsibilities, clarify roles and set expectations. Use checklists and regular audits to maintain accountability. This structured approach not only improves compliance but also frees up attorneys to focus on client work.
Tax Planning and Year-End Preparation
Strategic tax planning is a vital element of accounting for law. Track deductible expenses throughout the year and use automated systems to categorize transactions. Preparing for quarterly and annual filings reduces surprises and maximizes tax advantages.
Leverage year-end financial reports to identify areas for cost savings or investment. This process is made easier with specialized legal accounting software and clear documentation protocols. For step-by-step guidance, refer to Year-End Law Firm Financial Best Practices for 2025.
A proactive approach to accounting for law during year-end ensures your firm remains compliant and financially agile. Focus on timely reconciliations, organized records, and ongoing tax education for your team.
Staying Ahead of Regulatory and Industry Changes
Accounting for law is an ever-changing field, with new rules and best practices emerging regularly. Stay informed by monitoring updates to trust accounting and tax laws through bar associations and industry publications.
Participate in continuing education programs and consider joining professional groups focused on legal finance. Implementing flexible accounting systems helps your firm adapt quickly to new requirements, avoiding last-minute scrambles.
Firms that stay ahead of regulatory shifts maintain client trust and avoid penalties. By making ongoing learning and process improvement a core part of your accounting for law strategy, you ensure your practice is prepared for the future.
Future Trends in Law Firm Accounting
The landscape of accounting for law is evolving rapidly as 2025 approaches. Law firms must adapt to new regulations, technological advancements, and shifting client expectations. Here are the key trends shaping the future of legal accounting.
The Impact of Regulatory Changes and Industry Shifts
Regulatory requirements in accounting for law are becoming more complex each year. State bars and federal agencies are increasing scrutiny on trust accounts and client fund management. Law firms should expect updates to reporting standards and possibly new digital audit protocols in 2025.
For example, some states may require more frequent reconciliations or enhanced documentation for IOLTA accounts. Staying proactive with compliance ensures firms avoid costly penalties and maintain credibility.
The Rise of Automation and AI in Legal Finance
Automation and AI are transforming accounting for law by streamlining processes and reducing manual errors. Predictive analytics tools now help firms forecast revenue and assess financial risks more accurately.
AI-driven systems can monitor compliance and detect irregularities in real time. Firms that embrace these technologies gain efficiency, minimize risk, and free up staff for higher value tasks within their accounting for law workflows.
Evolving Client Expectations and Transparency
Clients now expect real-time access to billing information and transparent financial statements. In accounting for law, this means offering secure client portals and digital payment options.
Firms that prioritize transparency build stronger client relationships and improve retention. Providing up-to-date account status and clear communication becomes a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital world.
Remote Work and Virtual Financial Management
Remote and hybrid work models are here to stay for law firms. This shift is driving the adoption of cloud-based accounting for law solutions.
Virtual bookkeeping allows easy collaboration with financial experts regardless of location. Firms benefit from flexibility, lower overhead costs, and access to specialized knowledge, all while maintaining robust financial controls.
Continuous Education and Professional Development
Staying current in accounting for law requires ongoing education. Regulatory guidelines and best practices are always changing, making training essential for legal finance teams.
Firms investing in certification programs, industry webinars, and regular staff training experience fewer compliance issues. Knowledgeable teams are better prepared for audits and can implement new accounting for law standards more effectively.
Preparing for the Next Decade in Legal Accounting
Future-ready firms are already building adaptable systems to meet evolving regulatory, technological, and market demands. Embracing innovation and strategic planning will set leaders apart in the field of accounting for law.
You didn't invest in legal education and build a practice to manually track bank balances, categorize business expenses, or monitor accounts receivable. Yet DIY bookkeeping constrains you to precisely these functions. It positions you in a reactive posture rather than enabling strategic growth.
Clean books. Accurate financial records. Audit-ready trust accounts. Strategic financial statements. When your financial systems deliver these foundational elements - you position your law firm for business growth rather than merely sustaining a practice.
When you're prepared to delegate financial operations and accelerate growth, we're positioned to implement a sophisticated legal accounting process tailored to your firm.
Contact us today!