5 Ecommerce Bookkeeping Mistakes That Kill Your Profit
Ecommerce bookkeeping mistakes slip into financial records more easily than most business owners expect. A deposit from Shopify or Amazon may look like pure revenue, but fees, refunds, and chargebacks quietly reduce the actual number. These errors distort financial statements and erode profit margins without showing obvious warning signs.
When ecommerce businesses fail to track costs at the SKU level or mix personal and business expenses, margins break down and cash flow becomes unreliable. Accounting mistakes like mishandling sales tax across marketplaces or ignoring payment processing fees create compliance risks and skew profitability. Over time, messy bookkeeping hides the true financial health of an e-commerce business.
Accurate accounting protects margins, supports growth, and prevents costly surprises. With the right systems in place, ecommerce businesses can avoid the most common bookkeeping mistakes and gain clear visibility into performance. The difference between thriving and struggling often comes down to disciplined financial management.
Our ecommerce bookkeeping services help Shopify and Amazon sellers avoid costly reporting errors from day one.
Mistake #1: Treating Shopify/Amazon Deposits as Revenue - Ignoring Payment Processing Fees and Refunds
Shopify and Amazon deposits represent a mix of transactions, not pure sales. Each payout includes deductions for fees, refunds, and sometimes chargebacks, which means the bank deposit rarely matches the true revenue earned. Recording only the deposit amount distorts financial statements and creates inaccurate profit margins.
Why Marketplace Payouts ≠ Actual Revenue (Fees, Refunds, Chargebacks)
Marketplace deposits are net amounts, not gross sales. A single payout may include:
Gross sales revenue
Payment processing fees
Marketplace commissions
Refunds and returns
Chargebacks
Sales tax collected
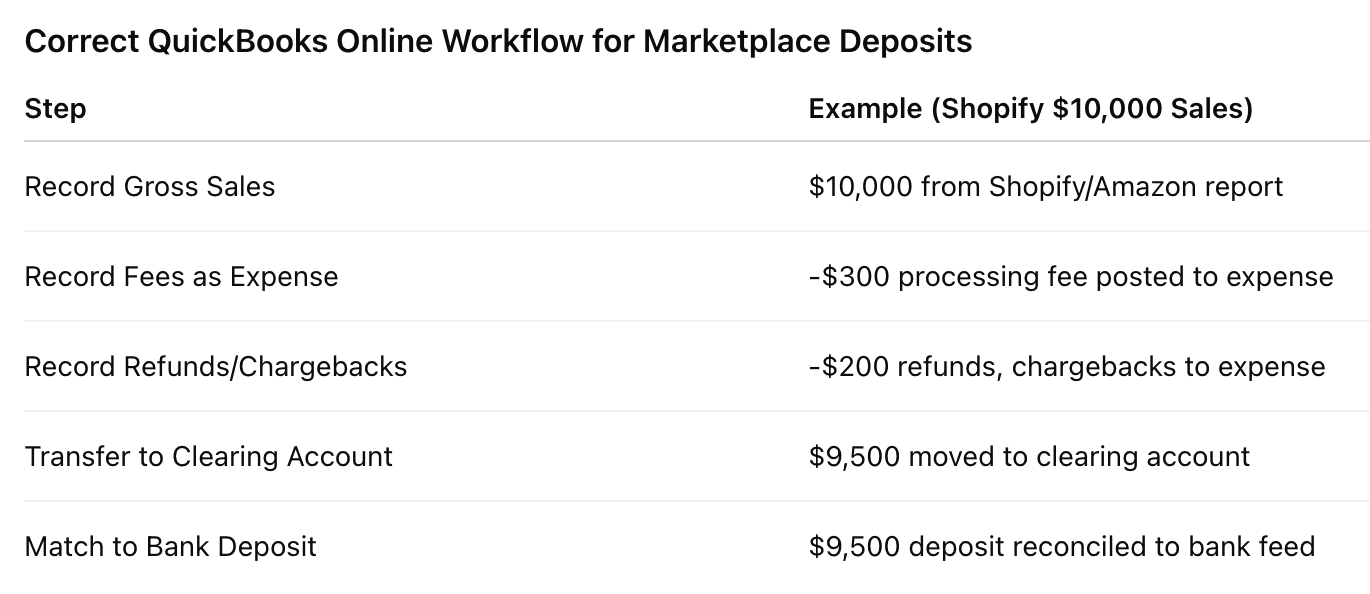
For example, if a seller generates $10,000 in sales, Shopify may deduct $300 in processing fees and $200 in refunds before sending an $9,500 deposit. Recording $9,500 as revenue understates sales and hides true operating costs.
This mistake leads to financial statements that misstate both income and expenses. Deposits are not revenue - they are settlements after adjustments. Without properly separating these components, businesses risk compliance issues and poor decision-making.
QuickBooks Online Workflow: Clearing Accounts and Financial Reports
The correct workflow in QuickBooks Online uses a clearing account. Instead of booking the bank deposit directly as income, sellers should:
Record gross sales from Shopify or Amazon reports.
Post fees, refunds, and chargebacks as separate expense categories.
Transfer the net balance to match the actual bank deposit.
This method ensures that financial reports reflect both top-line sales and related costs. Reconciling through clearing accounts allows owners to see accurate gross revenue, expenses, and net income without confusion.
Tools that integrate with QuickBooks can automate this process, breaking down deposits into detailed components. Automation reduces errors and provides clarity when reviewing profit and loss statements.
Mistake #2: No SKU-Level Cost of Goods Sold - Broken Margins and Bad Inventory Costs
Without SKU-level cost tracking, cost of goods sold becomes a guess, margins lose accuracy, and financial reports misstate profitability. Errors in setup, recording, and reporting flow through to tax filings, cash flow planning, and pricing decisions.
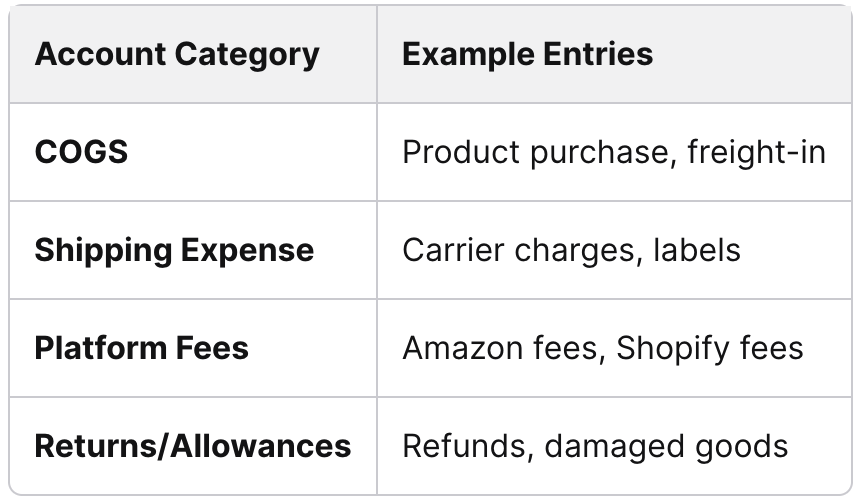
Chart of Accounts Setup for COGS, Shipping, Platform Fees, Returns
A precise chart of accounts separates direct costs from indirect expenses. Cost of goods sold (COGS) should capture product costs only - purchase price, freight-in, duties, and packaging. Shipping to customers, platform fees, and returns belong in their own accounts.
When these costs blend together, margin analysis breaks down. For example, recording Shopify fees as COGS inflates product costs and hides true gross profit. A clear structure allows management to see if issues stem from high fulfillment costs, poor pricing, or supplier increases.
A sample breakdown might include:
This separation ensures SKU-level reporting ties back to accurate financial statements.
Using Inventory Management Software/System to Track Costs Accurately
Manual spreadsheets rarely capture true inventory valuation. Modern inventory management software such as Cin7 or Fishbowl assigns costs at the SKU level, supports FIFO or weighted average, and integrates with accounting platforms.
Accurate tracking requires linking purchase orders, receipts, and sales orders. When systems track landed costs per SKU, COGS reflects reality rather than estimates. This prevents overstating expenses when inventory is purchased but not yet sold, a common ecommerce mistake.
Automated systems also handle returns and restocks correctly, preventing duplicate costs. By syncing inventory data with accounting records, founders gain real-time margin visibility. This allows for timely pricing adjustments and better supplier negotiations.
How Poor Cost Tracking Distorts Profit and Loss Statements
When SKU-level COGS is missing, financial statements lose their reliability. Overstated inventory reduces COGS, inflating net income. Understated inventory does the opposite, overstating expenses and reducing reported profit. Both errors distort cash flow forecasts and tax liabilities, as explained in inventory error adjustments.
Profit and loss statements built on inaccurate costs mislead decision makers. A business may think certain products are profitable when they are not. Conversely, profitable SKUs may appear unviable if costs are misallocated.
This distortion prevents leaders from knowing whether problems lie in sales strategy, supplier pricing, or fulfillment. Reliable SKU-level cost tracking is the only way to ensure margins reflect actual business performance.
With organized, trustworthy bookkeeping, you’ll catch issues like poor cash flow management before they sink your business.
Mistake #3: Poor Cash Flow Management - Sales Up, Cash Down
Many ecommerce businesses show strong sales but struggle to pay bills on time. The problem often lies in how cash flow is tracked, forecasted, and managed, not in revenue generation itself.
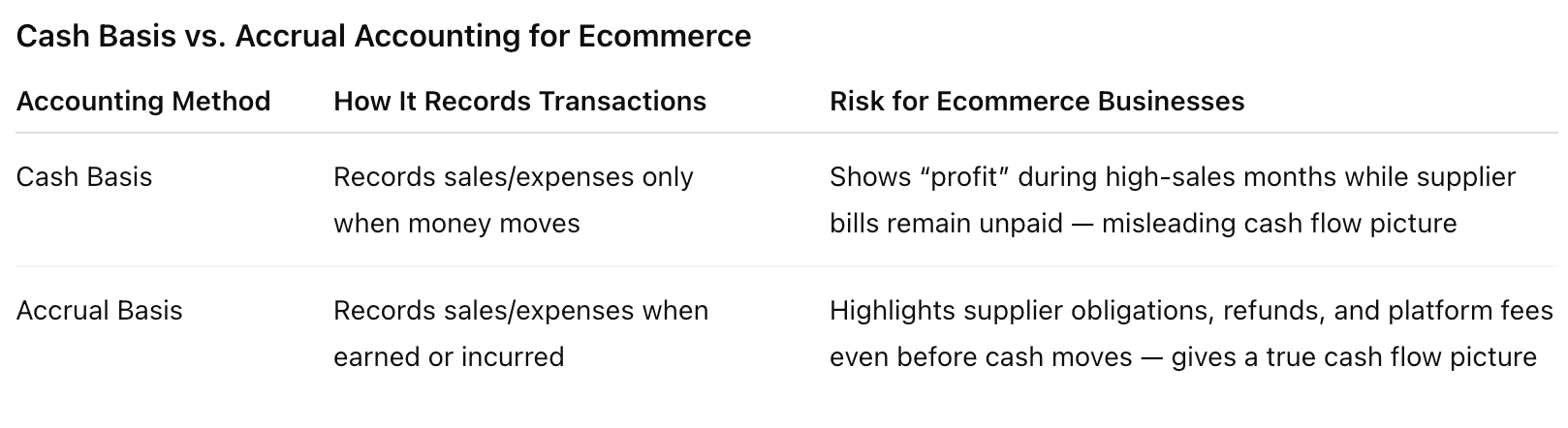
Cash Basis Accounting vs. Accrual Accounting for Ecommerce Businesses
Choosing the wrong accounting method can distort cash flow. Cash basis accounting records money only when it enters or leaves the bank. This approach is simple but can mislead owners during high-sales periods when receivables are still unpaid.
Accrual accounting records revenue and expenses when earned or incurred, not when cash moves. For ecommerce, this method gives a clearer picture of obligations such as supplier invoices, returns, and platform fees.
Consider this scenario: a store sells $50,000 in one month but has $40,000 in pending supplier payments. Cash basis may show a profit, while accrual highlights the upcoming cash shortage. This difference directly affects cash flow management and financial planning accuracy.
Building a Cash Flow Statement and Forecast to Avoid Shortages
A cash flow statement tracks actual inflows and outflows. It separates activities into three categories:
Operating (sales, refunds, supplier payments)
Investing (equipment, software, or inventory purchases)
Financing (loans, credit repayments, or equity contributions)
Without this structure, owners often underestimate how much money is tied up in inventory or delayed by payment processors.
A cash flow forecast projects future balances based on expected sales, vendor terms, and recurring expenses. This forecast allows ecommerce businesses to anticipate gaps before they occur. Tools and structured reporting, such as monthly profit and loss statements and cash flow summaries, are recommended by experts to prevent common ecommerce accounting mistakes.
Even a 90-day forecast can help a founder schedule marketing campaigns, negotiate better supplier terms, or delay nonessential spending.
Signs of Poor Cash Flow Management That Sink Ecommerce Businesses
Several warning signs indicate weak cash flow management:
Frequent reliance on short-term loans or credit cards
Inability to cover payroll or supplier invoices on time
Large inventory sitting unsold while cash reserves shrink
Lack of a reserve fund for slow sales months
Studies show that 82% of small business failures stem from cash flow problems. Ecommerce owners often overlook delayed customer payments, high return rates, or platform fees until liquidity becomes critical.
When these issues compound, businesses may appear profitable on paper but still face insolvency. Recognizing these signals early and implementing structured financial management practices prevents the downward spiral described in common cash flow mistakes.
Mistake #4: Mishandling Sales Tax - Collecting, Filing, and Rates Across Marketplaces
Sales tax rules differ by state, product type, and sales channel, creating risks for ecommerce sellers who fail to track obligations carefully. Errors in collection, filing, or rate application can lead to penalties, audits, and unnecessary liabilities.
Sales Tax Obligations and Nexus Rules for Ecommerce Sellers
Ecommerce sellers must understand where they have nexus, which is the legal connection requiring them to collect and remit sales tax. Nexus can arise from physical presence, such as inventory stored in a warehouse, or from economic thresholds like revenue or transaction counts in a state.
For example, selling through Amazon FBA often creates nexus in multiple states because inventory is distributed across fulfillment centers. Many businesses overlook this, leading to uncollected tax and exposure to back payments.
States frequently update their requirements, and sellers must monitor changes to avoid noncompliance. Common mistakes include assuming sales tax only applies in the company’s home state or failing to register in states where thresholds are exceeded.
A clear process for tracking nexus ensures compliance. Businesses that ignore these rules risk penalties similar to those outlined in common sales tax errors.
Filing Sales Tax Correctly During Tax Season
Collecting tax is only the first step. Sellers must also file returns on time, in the correct format, and for the correct jurisdictions. Missing deadlines or submitting filings with errors can result in fines or interest charges.
Different states require monthly, quarterly, or annual filings depending on sales volume. Businesses selling across multiple marketplaces may need to file in several states at once, which increases the chance of mistakes.
Frequent errors include reporting gross sales instead of taxable sales, misclassifying exempt transactions, or failing to reconcile collected tax with amounts remitted. Guidance from resources like sales tax compliance mistakes shows how these small oversights can lead to large liabilities.
Maintaining a compliance calendar and using tax software reduces manual errors and keeps filings consistent.
Using QuickBooks Online and Accounting Software to Manage Tax Liabilities
Accounting software plays a critical role in managing sales tax obligations. QuickBooks Online, for example, can track sales tax by jurisdiction, apply the correct rates, and generate reports that match filing requirements.
When integrated with ecommerce platforms, these tools provide real-time visibility into tax liabilities. This reduces the risk of underpayment or overpayment and helps ensure that collected funds are set aside for remittance.
Automation also simplifies reconciliation. Instead of manually reviewing each transaction, sellers can rely on built-in features to match collected tax with filings. This is especially useful for businesses selling on multiple marketplaces where rates vary.
Using accounting software for sales tax compliance not only saves time but also creates reliable records in case of an audit. Proper setup and regular review of system settings are essential to avoid errors in rate application or reporting.
Many ecommerce businesses fail because they lack clean, dependable financial support that keeps financial statements accurate.
Mistake #5: Messy Books - Commingled Personal and Business Expenses, Loose AP/AR, and a Generic Accounting System
When financial records are disorganized, owners lose clarity on cash flow, tax obligations, and profit margins. The most common problems include mixing personal and business expenses, failing to control accounts payable and receivable, and relying on a one-size-fits-all accounting system.
Why Separating Personal and Business Expenses Is Non-Negotiable
Mixing personal and business finances creates confusion that weakens decision-making. Without a dedicated business bank account, owners risk overstating deductions, misreporting taxable income, and drawing IRS scrutiny.
Commingling also complicates audits and due diligence. Investors and lenders expect clean financial statements. A clear separation of business expenses ensures credibility and reduces liability.
Maintaining distinct accounts also protects personal assets. If records show blurred lines between personal and business spending, legal protections like limited liability can be challenged. This is especially critical for ecommerce founders who may rely on corporate structures for risk management.
Simple practices—such as using a business-only credit card and reconciling accounts monthly - prevent these issues. Commingling creates long-term complications that outweigh short-term convenience.
Cleaning Up Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, and Financial Transactions
Disorganized accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR) cause cash flow strain. Late payments to vendors damage relationships, while uncollected receivables tie up working capital.
Owners should establish clear payment terms, track invoices in real time, and reconcile AR weekly. Spreadsheets often fail at scale; accounting software with automated reminders reduces errors and improves collection rates.
On the AP side, structured approval workflows prevent duplicate or missed payments. Reviewing outstanding bills monthly keeps liabilities visible and predictable.
A disciplined bookkeeping process ensures that every transaction is categorized correctly. As highlighted by accountingprofessor.org, messy financials can be avoided by reconciling accounts regularly and separating personal and business expenses.
The Role of a Tax Professional in Protecting Financial Health
A tax professional helps untangle disorganized books and prevent costly mistakes. When personal and business transactions overlap, an accountant can reclassify expenses and restore clean records.
They also ensure compliance with tax laws, maximizing deductions without triggering red flags. For ecommerce businesses, where online sales tax rules vary by state, professional oversight is essential.
Beyond compliance, a tax advisor provides strategic planning. They evaluate AP/AR trends, recommend accounting systems tailored to business needs, and identify risks before they escalate.
Working with a qualified advisor is the best way to rectify commingling and establish stronger financial practices. This guidance protects long-term financial health and safeguards against penalties.
How These Mistakes Erode Financial Health (And What to Do Next)
Small errors in bookkeeping compound into larger financial problems. Missed reconciliations, poor expense tracking, and inaccurate statements weaken decision-making and reduce long-term stability. Correcting these issues starts with clear audits, measurable impact reviews, and disciplined systems.
Quick Audit Checklist for Financial Records and Reports
A structured financial review highlights where records fall short. Owners should begin by confirming that bank statements match accounting software each month. Any gap signals misreporting or cash flow blind spots.
Next, examine whether accounts receivable and payable reports are current. Late updates distort financial statements and hide liquidity risks. Inventory records must also align with sales reports to prevent overstated profits.
Tax obligations form another critical checkpoint. If sales tax filings or estimated quarterly payments are inconsistent, penalties accumulate quickly. Businesses often overlook this until notices arrive.
Finally, review whether profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow reports are generated consistently. Regular reporting ensures management sees the true financial health, not just top-line revenue. Conducting this checklist quarterly reduces errors before they erode working capital.
Table: Estimated Profit Impact by Mistake
The table below outlines common ecommerce bookkeeping mistakes and their potential effect on net profit margins. While exact figures vary, these ranges reflect patterns seen in small and mid-sized sellers.
Studies show that over 80% of online businesses struggle with financial mismanagement. Quantifying the impact helps owners prioritize which gaps to correct first.
Organized, Trustworthy Bookkeeping for Ecommerce Sellers
Founders who want stronger financial health must replace reactive fixes with structured bookkeeping. This means maintaining timely reconciliations, scheduled financial reviews, and reliable documentation of every transaction.
An organized system builds accurate financial statements that lenders, investors, and tax authorities trust. It also gives owners confidence in scaling decisions without hidden risks.
For ecommerce sellers, the next step is simple: implement disciplined bookkeeping practices or work with a partner who ensures compliance and clarity. Reliable records protect profit margins, reduce stress, and position the business for sustainable growth.
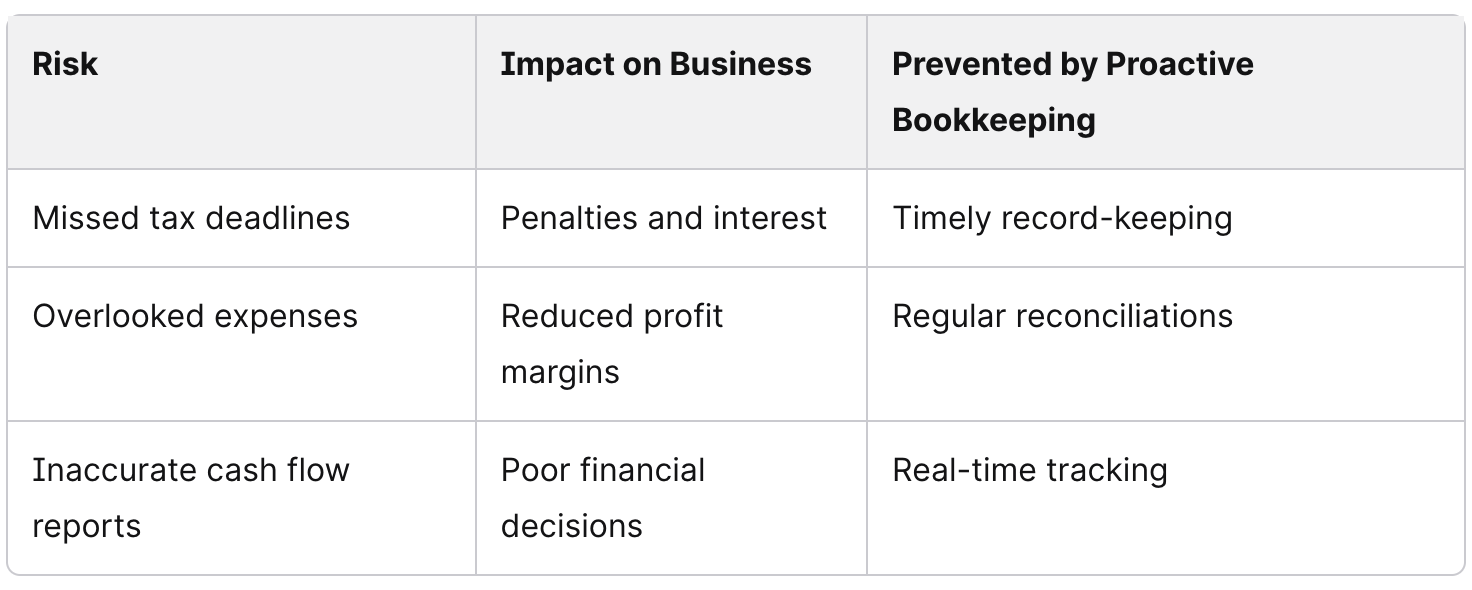
Why Proactive Bookkeeping Prevents Costly Mistakes
Proactive bookkeeping gives business owners clarity before problems arise. By tracking transactions in real time, they reduce the chance of missed payments, late fees, or inaccurate reports. This approach protects cash flow and keeps financial records ready for tax deadlines.
Key benefits include:
Early detection of errors
Stronger compliance with tax obligations
Reliable financial data for decision-making
Reduced stress during peak sales periods
Even small errors can grow into larger financial issues. In ecommerce, overlooked expenses or uncollected payments often lead to reduced margins. Consistent, proactive bookkeeping helps prevent these costly mistakes by keeping data accurate and up to date.
Professional support adds another layer of protection. A skilled bookkeeper ensures automation tools are set correctly, reconciliations are completed on schedule, and reporting stays consistent.
By adopting a forward-looking approach, businesses build a stronger financial foundation. Proactive bookkeeping limits unnecessary costs, supports compliance, and provides the accurate numbers leaders need to grow with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ecommerce Bookkeeping Mistakes
-
Misclassifying platform fees, skipping account reconciliations, mishandling sales tax, and poor inventory tracking are common ecommerce bookkeeping mistakes. Each error distorts profit margins and financial reports, creating risks for compliance and growth.
-
Without regular reconciliations, discrepancies between bank deposits, Shopify/Amazon payouts, and accounting records go unnoticed. This leads to overstated balances, hidden transaction errors, and unreliable financial statements.
-
Incorrectly collecting or filing sales tax creates compliance liabilities. Sellers risk penalties, audits, and disrupted cash flow. Accurate sales tax compliance - tracked through accounting software - prevents these costly mistakes.
-
Inadequate inventory tracking misstates cost of goods sold (COGS) and profit margins. Sellers risk over-ordering, stockouts, and distorted financial reporting. Proactive inventory management software keeps COGS and profit accurate.
-
Combining personal and business transactions clouds financial health, complicates tax filings, and hides true profitability. Separate accounts maintain compliance and reliable financial statements.
-
Underutilized software leaves sellers exposed to manual errors, untracked fees, and incomplete financial data. Leveraging QuickBooks Online and ecommerce-specific integrations ensures accurate reporting and automation.